INL Cyber SHIELD for Renewables
Security through Hardware Integration, Education, and Layered Defense
An Idaho National Laboratory (INL) initiative aimed at helping owner/operators of renewable energy generation secure and protect infrastructure and ensure the transition to the renewable energy grid of the future is secure.

Become a Cyber SHIELD Partner
Let us help you chart a more secure cyberinfrastructure path.
The INL Cyber SHIELD Program is funded by the Department of Energy, and is a collaborative effort between the Wind Energy Technologies Office (WETO), Water Power Technologies Office (WPTO), and Solar Energy Technologies Office (SETO).
INL Cyber SHIELD tools and assessments are open-source, and INL-hosted engagements are available to utility-scale renewable owner/operators.
Direct Benefits for Renewables Asset Owner/Operators
- Understanding Asset-Level Risks: Understand Asset-Level Risks: Gain a better understanding of your assets, your asset-level risks, devices, protocols, vulnerabilities, and potential misconfigurations.
- Identification of System Weaknesses and Vulnerabilities: Identify potential attacks, vulnerabilities and active exploits specific to your assets/devices.
- Increased Network Reliability: Increase network visibility to enable more informed decisions and improve reliability.
- Guided Cybersecurity Assessment: Together, through guided cybersecurity assessment, we will produce a risk-based report to enhance cybersecurity programs leveraging established frameworks tuned for the renewable asset sector.
- Network Architecture Mapping: Gain the ability to map network architecture within the assessment to control areas to help identify or validate your cyber posture.
- Expert Cyber Program Support: Immediate access to supporting cyber programs and resource planning capabilities to quickly meet maturity objectives.
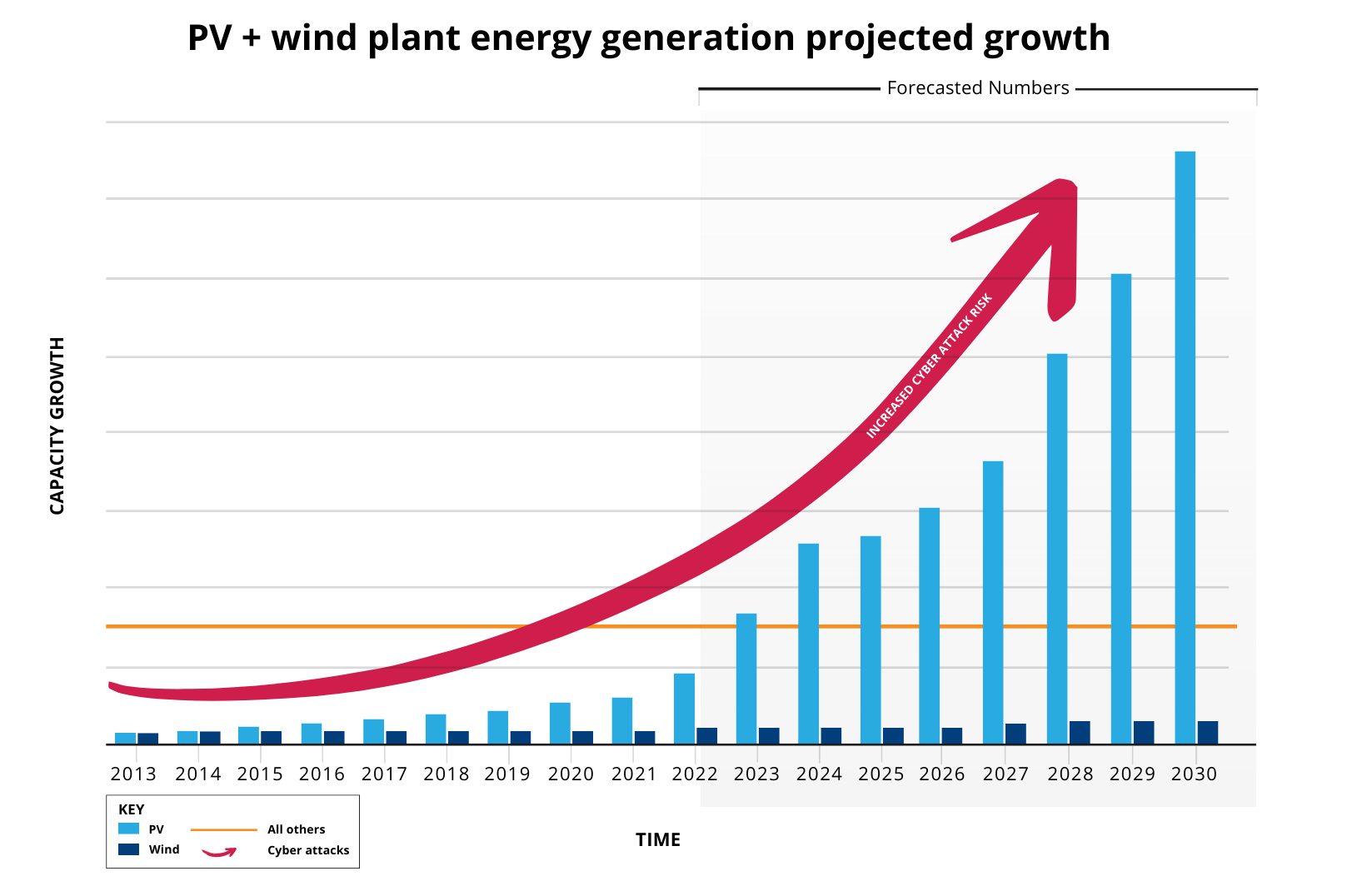
The INL Cyber SHIELD initiative aims to improve cybersecurity for renewable energy sources and ensure the security of future grids. By leveraging robust tools developed under Department of Homeland Security (DHS) programs, the initiative seeks to raise the floor in cybersecurity for renewables and accommodate any level of cyber maturity. The mission is to protect renewable energy infrastructure from cyber risks by deploying risk analysis tools. Within a decade, renewables are expected to become the leading generation source in our grids. The program is available to all renewable asset owner/operators.
Available INL Cyber SHIELD Program Benefits
Cybersecurity Threat and Risk Mitigation
The fast-paced evolution of technology and the growing cyber threat landscape highlight the need to improve security in the renewable sector to facilitate a successful transition.
Operational and Cybersecurity Resilience
Our program offers renewable energy owner/operators predictive tools to develop adaptation and resilience strategies that will allow them to address cyber threats in a proactive manner.
Types of Renewable Assets
Protecting the Grid
Regulatory Compliance
Implementation Process
Cyber Shield Tools
Further Reading
Collaborate with Cyber SHIELD
contact us
Renewable Assets Benefiting from Cyber SHIELD
The Cyber SHIELD Program is available as an INL-hosted assessment to all renewable asset owner/operators. Our tools are specifically tuned for use with renewable assets and can accommodate any level of cyber maturity. Our primary goal is to help owner/operators identify where they are on the resilience path and steps to take to improve their organization’s cyber maturity.

Wind Renewables
Wind energy production is expected to double to 20% of US electrical energy production by 2030. Wind energy is expected to grow to 35% by 2050, with a significant portion coming from offshore wind.
Solar Renewables
Solar energy is expected to be the largest growth driving an exponential scale from 3%-5% of total US electrical energy production to 30% by 2030. From 2024 to 2050, solar facilities will make up 80% of the expansion of renewables. This figure includes utility-scale and small-scale home solar systems.

Water Renewables
Hydroelectric plants account for approximately 6-7% of total US electrical energy production. As variable renewables continue to grow, our 2100 hydroelectric plants will be called upon to compensate to support the variability.
Inverter Based Energy Storage
Inverters are the power electronics in renewables (wind and solar) that convert direct current (DC) electricity, to alternating current (AC) electricity, which the electrical grid uses.
Renewable Energy’s Role and the Security Imperative
The number of generation plants will increase significantly over the next decades, correspondingly increasing the potential cyber attack surface. The rapid and frequent evolution of technology and the cyber threat landscape brings urgency to the importance of maturing security within the renewable sector to support the effective transition.
Regulatory Compliance & Legal Readiness
The future grid with renewables will look much different than today’s and will require more reliability standards. The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) has issued an order for reliability and registration standards for wind, solar, and storage in the future renewables grid. The order aims to protect the grid by focusing on unregistered resources that may have a material impact on the reliability of the Bulk-Power System. The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) may already register resources with an individual material impact.
FERC and NERC Critical Infrastructure Protection (CIP) Revisions include the following:
- Requirement(s) for authentication of remote users before access is granted to networks containing low-impact BES Cyber Systems at assets comprising those systems with external routable connectivity.
- Requirement(s) for protecting user authentication information (e.g., combinations of usernames and passwords) for remote access to low-impact BES Cyber Systems at assets containing those systems with external routable connectivity.
- Requirement(s) for detecting malicious communications to/between low-impact BES Cybers Systems at assets comprising those systems with external routable connectivity.
NERC Distributed Energy Resource Strategy
Distributed energy resource1 (DER) levels are rapidly growing across many areas of North America and are altering how the bulk power system (BPS) is planned, designed, and operated.

NERC Inverter-Based Resource Strategy
The rapid interconnection of bulk power system (BPS)-connected inverter-based resources (IBR) is the most significant driver of grid transformation and poses a high risk to BPS reliability.

NERC Security Integration Strategy
Cyber and physical security are critical facets of the bulk power system (BPS) reliability and resilience. Therefore, focusing on and mitigating these known and emerging risks is critical to the mission of the ERO Enterprise.
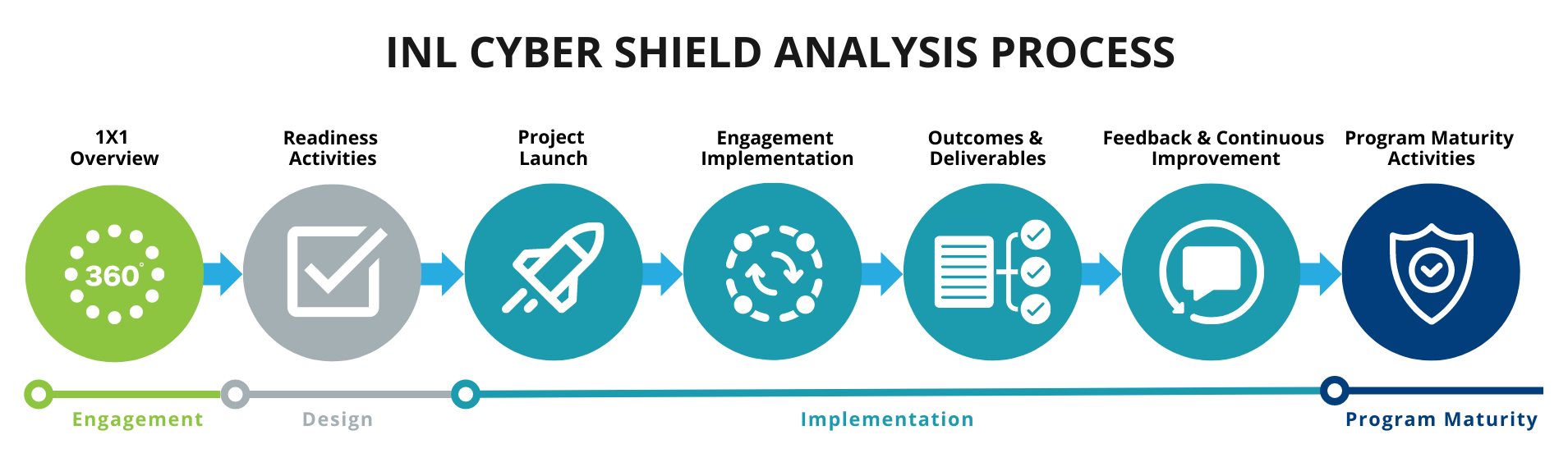
INL Cyber SHIELD Analysis and Implementation Process
INL Cyber SHIELD is designed to minimize the level of effort from your teams (understanding resources are often thin). Additionally, a key aspect of INL Cyber SHIELD is the ability to adjust to different levels of cybersecurity maturity levels, no matter what level of maturity you are this program and engagement can help guide your next steps in improving your cyber posture.
Customer information protection and confidentiality considerations have been integrated. Outcomes and deliverables focused on identifying risk, mitigation plans, and prioritization. The participants’ needs and resource availability guide the effort and duration engagement level.
To support the “raise the floor” objectives, the initial focus has been the deployment of three initiatives. These tools are designed to provide asset owner/operators with a step-by-step process to evaluate and mitigate cybersecurity risks, from performing a program assessment and mapping system architecture to a full asset interaction analysis toward cyber maturity.
INL Cyber SHIELD Renewables Cybersecurity Tools
Part of what makes INL Cyber SHIELD effective is the ability to adapt to different levels of cybersecurity maturity of organizations and drive to benefits. We leverage multiple robust tools developed under DHS programs. These tools are tuned for use with renewable assets and accommodate any level of cyber maturity with a primary goal of helping owner/operators identify vulnerabilities and chart a course to improve cyber maturity. The program’s cornerstone tools are the MALCOLM-AIA (Asset Interaction Analysis Tool) and the CSET (Cyber Security Evaluation Tool).
Provides renewable entities access to a cybersecurity assessment with cyber controls applied for OT environment providing risk-based recommendations for improving their maturity.

INL Malcolm-AIA – Asset Interaction Analysis: Leveraging Malcolm for the renewable industry. Passively deployable on your network to inks assets to business processes and translate the business processes to OT devices. Supports deeper threat and vulnerability identification/analysis for users. Geared to do the analysis and detection for you, simplifying many tasks.

The Cyber Security Evaluation Tool (CSET) provides a systematic, disciplined, and repeatable approach for evaluating an organization’s security posture. CSET is a desktop software tool that guides asset owners and operators through a step-by-step process to evaluate industrial control system (ICS) and information technology (IT) network security practices. Users can evaluate their own cybersecurity stance using many recognized government and industry standards and recommendations.
Further Reading: Renewable Energy Cybersecurity Trends
Insurance Policy and Commercial Litigation Trends – No More Wiggle Room
Cyber Insurance professionals will often need to assess the policy-readiness of their clients by examining their current cyber hygiene management according to a set of minimum requirements:
“As the name suggests, the Zero-Trust framework works on the basis that no activity of an organizational network is immune from thorough, ongoing security checks. In practice, it is a security approach that requires all users of an organization’s network and third-party providers with continuous access to the network, to be authenticated and authorized on an ongoing basis for security posture before being granted access to applications and data.”
The following resources and articles provide a deeper dive into the renewable energy cybersecurity challenges we face and an overview of recommendations designed to address critical renewable energy infrastructure challenges in the near term.
 NERC Low Impact Review Report
NERC Low Impact Review Report
NERC Low Impact Criteria Review Team White Paper, October 2022
 Department of Energy Report
Department of Energy Report
Cybersecurity Considerations for Distributed Energy Resources on the U.S. Electric Grid
 NERC Inverter-Based Resource Strategy
NERC Inverter-Based Resource Strategy
Ensuring Reliability of the Bulk Power System with Increased Levels of EPS-Connected IBRs
 Utility Dive Brief
Utility Dive Brief
FERC orders reliability standards, registration requirements for wind, solar, storage to protect the grid, November 2022
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Cyber SHIELD (INL Cyber SHIELD)?
Cyber SHIELD is an initiative developed by Idaho National Labs to raise the floor of cybersecurity for renewables. The initiative focuses on developing a suite of tools, programs, and resources customized for the renewable industry to improve cybersecurity posture and understand cyber risk better.
What tools is Cyber SHIELD based upon?
Cyber SHIELD is developed upon broader tools such as Cyber Security Evaluation Tool (CSET) and Malcolm, both of which are open source and DHS-sponsored tools.
What are cybersecurity assessment tools for the renewable industry?
The Cyber SHIELD initiative leverages multiple robust tools developed under DHS programs. These tools are tuned for use with renewable assets and accommodate any level of cyber maturity with a primary goal of helping owner/operators identify where they are and where to go to improve cyber maturity.
What are the benefits of using Cyber SHIELD?
Cyber SHIELD helps gain a better understanding of assets, including devices, protocols, and configurations, to identify potential cyber-attacks, vulnerabilities, and active exploits with more precision. This increases network visibility, enables informed decisions, and improves reliability. In addition, the ability to map network architecture within the assessment helps identify or validate the cyber posture. It provides immediate access to input supporting cyber programs and resource planning capabilities to meet maturity objectives quickly.
What is the level of effort required by asset owners/operators and asset stake holders for Cyber SHIELD engagements?
Asset owners/operators and asset stakeholders participating in Cyber SHIELD engagement should anticipate allocating time and resources for virtual introduction and technical exchange meetings, as well as onsite visits to support deployment tools and interviews with key personnel in order to properly evaluate participant cybersecurity posture.
Virtual Cyber SHIELD engagements are possible through remote assessment (over Microsoft Teams)
for renewable asset owners/operators and stakeholders that do not require network security
tools deployed in the participant ICS/OT environment (e.g., Malcolm deployment).
How can I get information on Cyber SHIELD?
Funding Partners
This work was funded by the Solar Energy Technology Office (SETO), the Wind Energy Technology Office (WETO), and the Water Power Technology Office (WPTO) which are part of the Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE).
Collaborate with INL Cyber SHIELD
The INL Cyber SHIELD team provides technical support and recommended best practices to renewable energy asset owners/operators and stakeholders to address cybersecurity gaps. This is accomplished through technical tool and processes to perform:
- Asset identification/discovery
- Threat detection
- Risk evaluation
Through Cyber SHIELD engagements, our goal is to enable the asset owner/operators and asset stakeholders to improve their cybersecurity and resilience to cyber threats.
Contact us to provide input or collaborate on the following topics:
- Developing cybersecurity and resilience strategies for the renewable energy sector
- Leveraging predictive cybersecurity tools to identify high-consequence cyber vulnerabilities and potential threats to asset owner/operator assets in the renewable energy sector
- Collaborating to enhance the INL Cyber SHIELD program to develop cybersecurity best practices and mitigation strategies for hardening of renewable energy infrastructure
To learn more about Industry Engagements with INL Cyber SHIELD, contact us at: [email protected]
